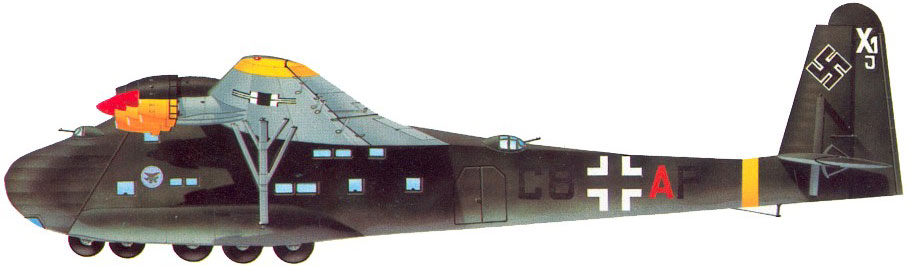
The Messerschmitt Me 323 Gigant ("Giant") was a German military transport aircraft of World War II. It was a powered variant of the Me 321 military glider and was the largest land-based transport aircraft of the war. A total of 213 are recorded as having been made, a few being converted from the Me 321.
Variants
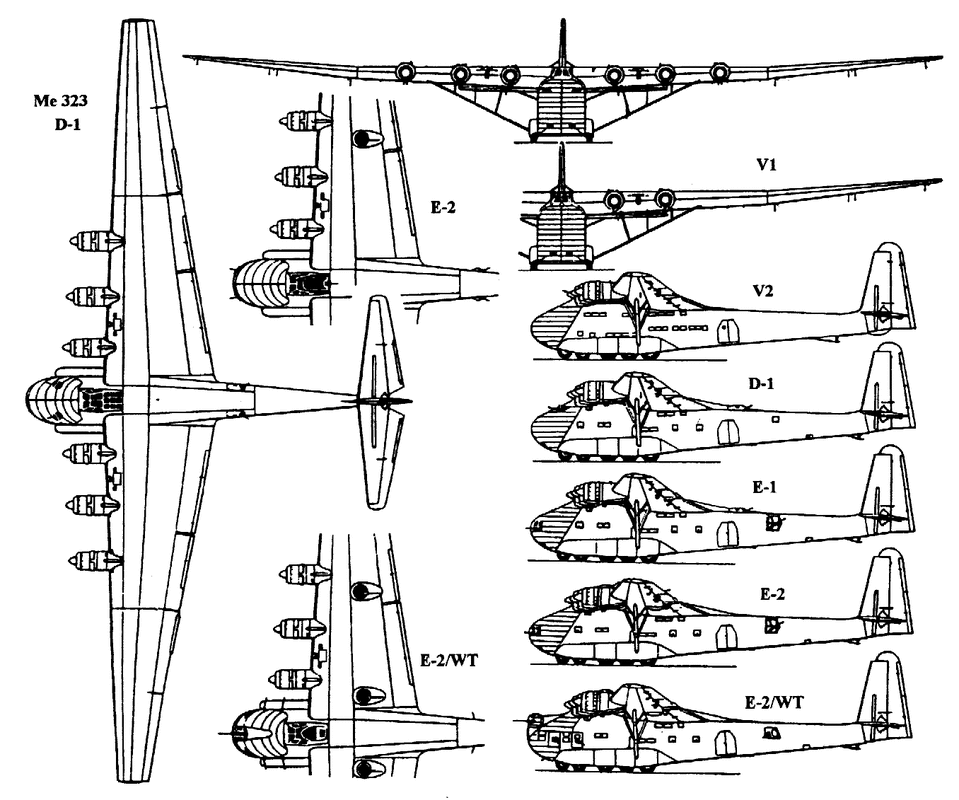
Me 323 V1
First Prototype, powered by four Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49 engines
Me 323 V2
Prototype, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines, became the standard for D production series
Me 323 D-1
First production series, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines originally intended for use in the Bloch 175, two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 15 machine guns in cockpit fittings provided, field modifications increased defensive armament, variable-pitch Ratier propellers with three blades
Me 323 D-2
as D-1 but with engine installation originally intended for use in the LeO 451, fixed-pitch wooden Heine propellers with two blades
Me 323 D-6
as D-2, variable-pitch Ratier propellers with three blades
Me 323 V13
Prototype, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines, served as a master for the Me 323E production series
Me 323 V14
Prototype, powered by six 1,340 PS Junkers Jumo 211F engines, not proceeded with
Me 323 E-1
Second production series, two gun turrets incorporated in the wings
Me 323 E-2
Proposed version with heavier armamentMe 323 E-2 WTProposed 'escort' gunship version, based on the E-1. Classified as a Waffentrager (weapons carrier) by the RLM, which the WT suffix denoted, in a similar role to that of the AmericanYB-40 Flying Fortress "gunship" heavy defensive fighter conversion for the USAAF. Primary mission was to provide normal 323 cargo formations with heavy defensive protection. No cargo carrying ability. "Solid" nose with 20mm cannon turret, two additional wing turrets plus up to ten other machine guns/cannon of varying calibres firing from standard and new waist/beam positions. 1.3 tonnes of armour plating was added across the entire airframe. Crew increased to twenty-one, the extra crew-members operating the plane's guns. Two prototypes built and tested, but series was cancelled after it was judged that normal single-engined fighters were more effective in the transport escort role. One of the prototypes was briefly assigned to KG 200 for operational evaluation, where it flew armed escort for the small number of captured B-17 Flying Fortresses operated by the Geschwader.
Me 323 V16
Prototype, powered by six 1,340 PS Jumo 211R engines, intended to serve as a master for the Me 323F production series
Me 323 V17
Prototype (unfinished), powered by six 1,600 PS (1,578 hp, 1,177 kW) Gnome-Rhône 14R engines, intended to serve as a master for the Me 323G
Me 323 Test Bed for Me 262
First Prototype, powered by four Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49 engines
Me 323 V2
Prototype, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines, became the standard for D production series
Me 323 D-1
First production series, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines originally intended for use in the Bloch 175, two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 15 machine guns in cockpit fittings provided, field modifications increased defensive armament, variable-pitch Ratier propellers with three blades
Me 323 D-2
as D-1 but with engine installation originally intended for use in the LeO 451, fixed-pitch wooden Heine propellers with two blades
Me 323 D-6
as D-2, variable-pitch Ratier propellers with three blades
Me 323 V13
Prototype, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14N engines, served as a master for the Me 323E production series
Me 323 V14
Prototype, powered by six 1,340 PS Junkers Jumo 211F engines, not proceeded with
Me 323 E-1
Second production series, two gun turrets incorporated in the wings
Me 323 E-2
Proposed version with heavier armamentMe 323 E-2 WTProposed 'escort' gunship version, based on the E-1. Classified as a Waffentrager (weapons carrier) by the RLM, which the WT suffix denoted, in a similar role to that of the AmericanYB-40 Flying Fortress "gunship" heavy defensive fighter conversion for the USAAF. Primary mission was to provide normal 323 cargo formations with heavy defensive protection. No cargo carrying ability. "Solid" nose with 20mm cannon turret, two additional wing turrets plus up to ten other machine guns/cannon of varying calibres firing from standard and new waist/beam positions. 1.3 tonnes of armour plating was added across the entire airframe. Crew increased to twenty-one, the extra crew-members operating the plane's guns. Two prototypes built and tested, but series was cancelled after it was judged that normal single-engined fighters were more effective in the transport escort role. One of the prototypes was briefly assigned to KG 200 for operational evaluation, where it flew armed escort for the small number of captured B-17 Flying Fortresses operated by the Geschwader.
Me 323 V16
Prototype, powered by six 1,340 PS Jumo 211R engines, intended to serve as a master for the Me 323F production series
Me 323 V17
Prototype (unfinished), powered by six 1,600 PS (1,578 hp, 1,177 kW) Gnome-Rhône 14R engines, intended to serve as a master for the Me 323G
Me 323 Test Bed for Me 262