Dornier Do 217N Schrage Musik
|
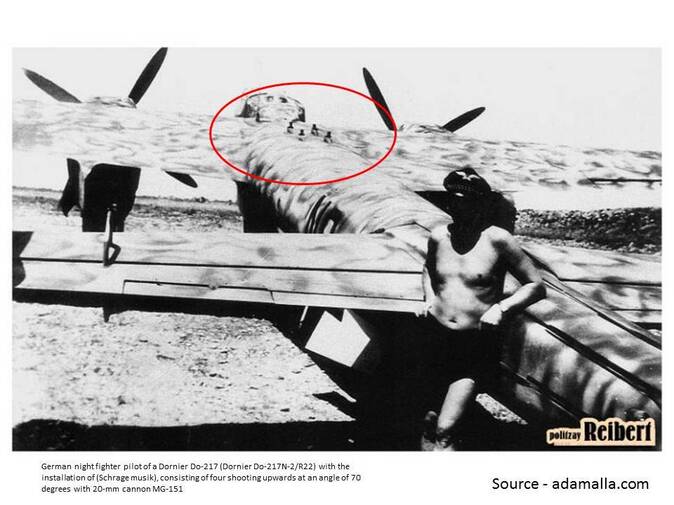
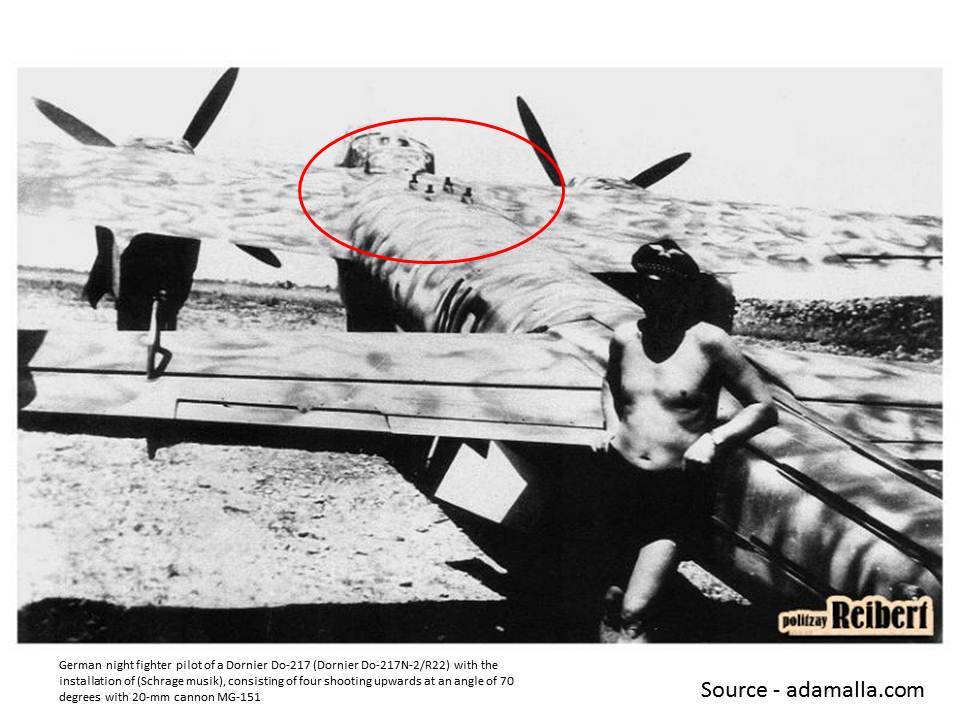
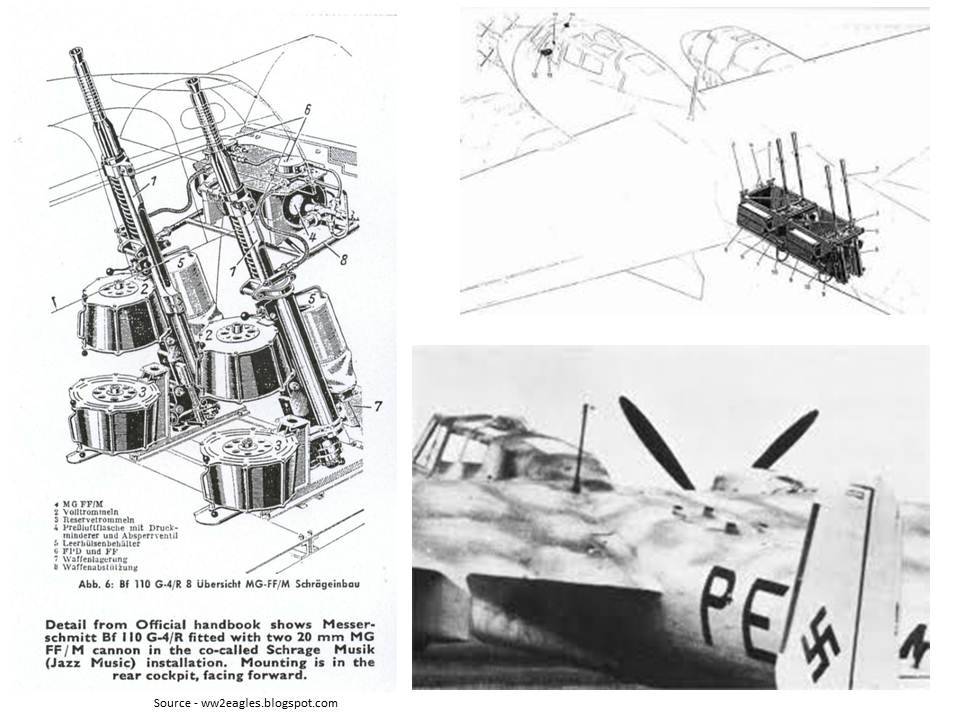
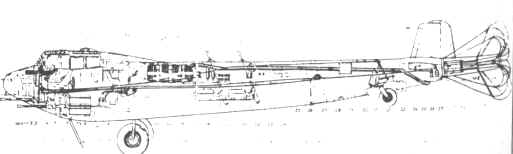
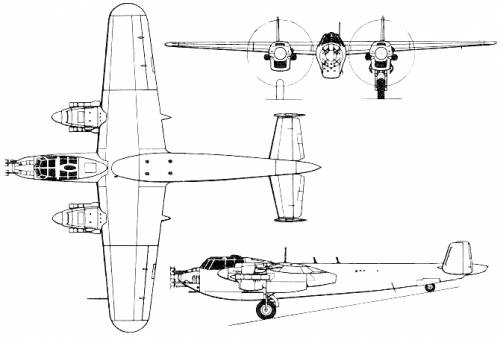
Do 217N: Night fighter based on the Do 217M. Armament similar to Do 217J but with improved 20 mm MG 151/20 cannons replacing the 20 mm MG FFs plus the addition of four 20 mm MG 151/20s as Schräge Musik.
Hauptmann Rudolf Schoenert of III./Nachtjagdgeschwader 3 suggested in July 1942, that trials be made of weapons slanting upwards at an angle of 70° (later known as Schräge Musik) in the fuselage. This entailed mounting four to six MG 151/20 autocannon in the centre of the fuselage. At Technisches Amt, two Do 217s, one with four and the other with six MG/151/20 cannon were ready for inspection on 5 August 1942 and testing in September. Schoenert built on it, with the introduction of the IR spanner and headlight, the bomber could approach from below a British bomber and avoid exposure to its powerful powered turrets guarding its tail, nose and upper fuselage by attacking from behind or head-on. British bombers did not have a ventrally-located Ball turret, and the new Dornier design attempted to take advantage. Other tactical improvements involved fitting a semi-rigid brake parachute in October 1942, allowing the Dornier to adjust to the speed of the bomber before firing on its target. The prototypes J-1/U2 and J-1/U4 were tested under these conditions. These designs were carried forward into the new variant, the Dornier Do 217N. Ten pre-production series N variants were designated as test beds. Trials began in the summer of 1942. On 16 August the second prototype Do 217, N V2, entered trials,. The N V1 and N V2 were the main testbeds. The third prototype, N-1/U was fitted with MG 151/20 and unspecified aerodynamic refinements. The machine was used in high-altitude de-icing tests, and the aircraft was tested with Lichtenstein BCR and Bernhardine radar. In August ten of these aircraft were constructed, and between 27 and 31 August, they were fitted with Schräge Musik. The tenth N variant, designated N-0, underwent radio trials. The machine was tested with the Peil G VI/APZ 6, a later and more sophisticated variant automatic direction-finding equipment. On 2 December further tactical trials were carried out with infrared target-illuminating equipment. |