|
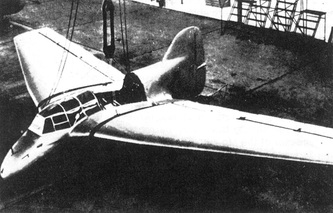
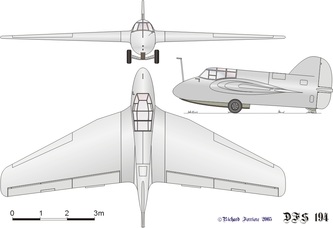
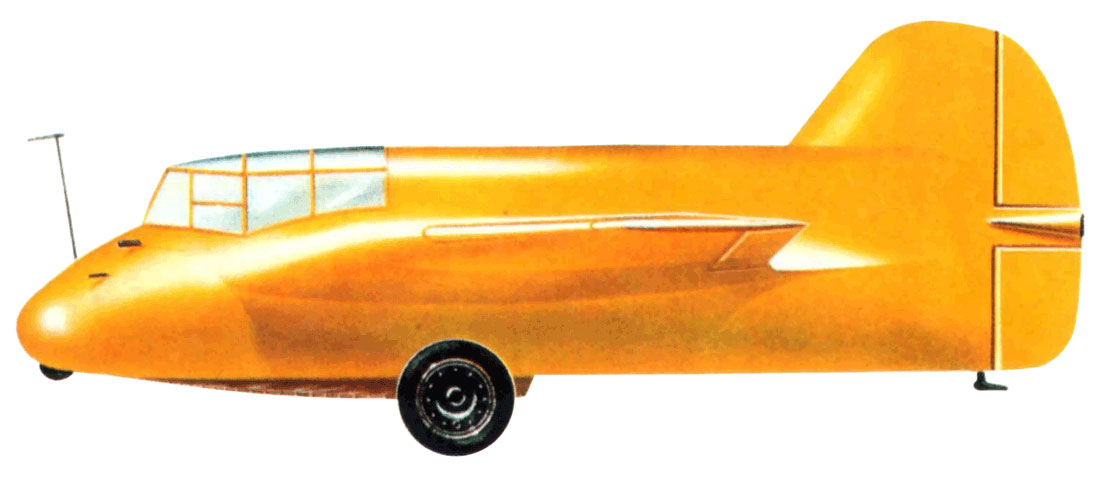
DFS 194
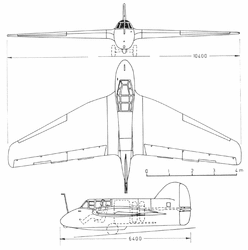
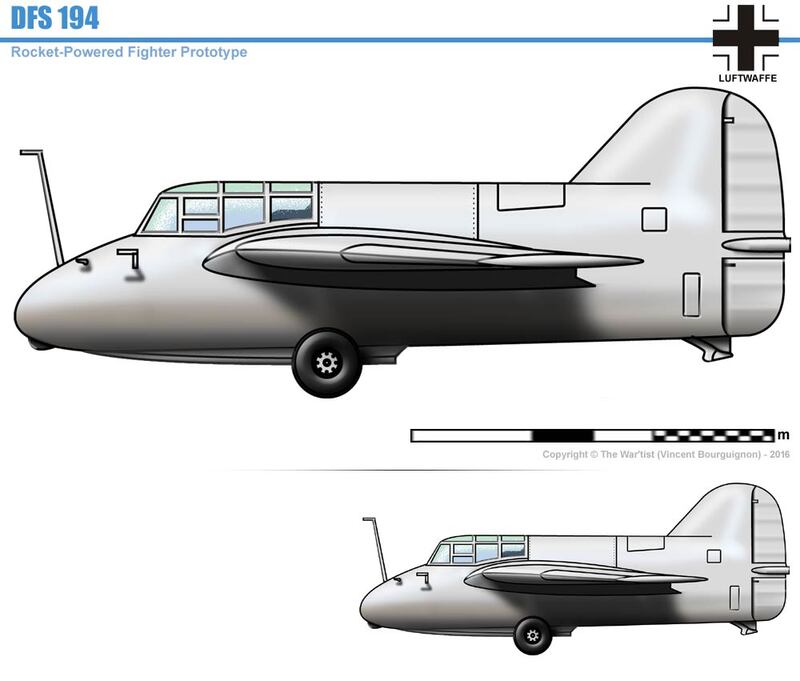
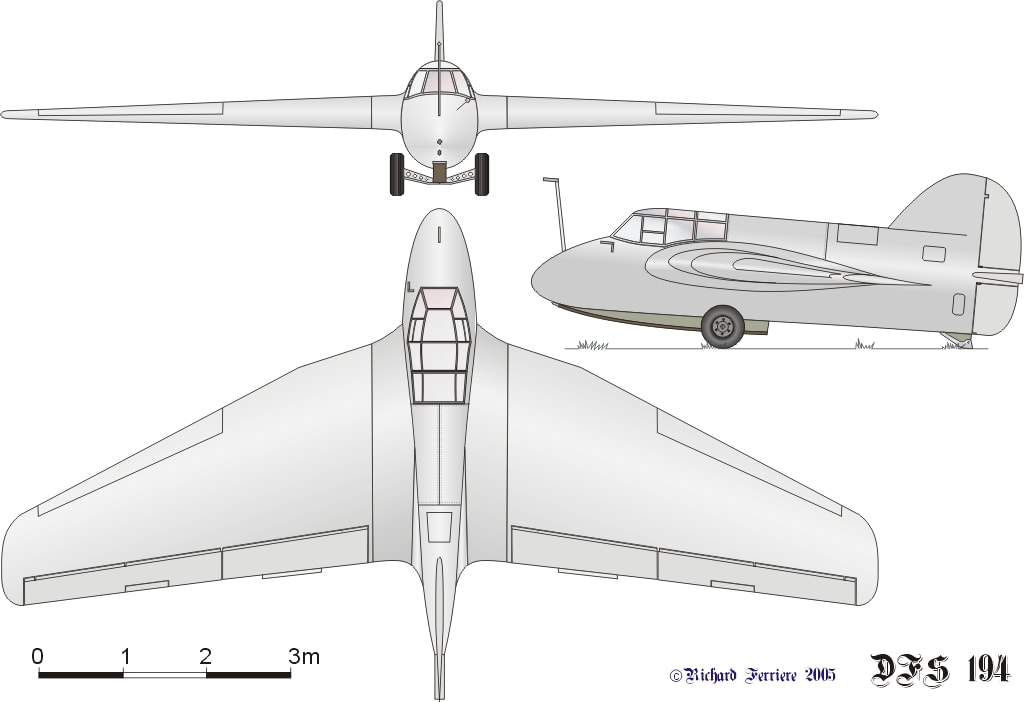
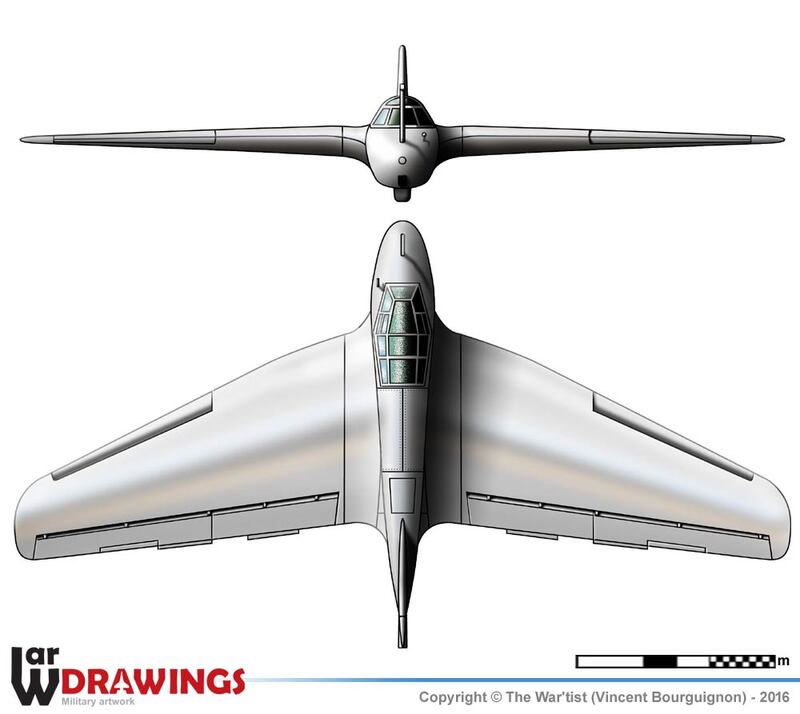
The DFS 194 was based on the Alexander Lippisch Delta series of tailless designs. As originally conceived, it would have been a tailless aircraft similar to his DFS 40, powered by a conventional piston engine driving a pusher propeller. The airframe was completed in this configuration in March 1938.
Lippisch's designs had attracted the attention of the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM - Reich Aviation Ministry) who believed that tailless aircraft were the best basis for a rocket-powered fighter. On January 2, 1939, Lippisch and his team were transferred to the Messerschmitt company to begin work on such an aircraft, under what was known as Project X.
The DFS-194 was modified to accept a Walter R I-203 rocket engine and by October, the aircraft was undergoing engine tests at Peenemünde. These were followed by glide tests in early 1940 leading to the first powered flight in August. The flight went well, the DFS 194 reaching 550 km/h (340 mph), bettering the speed of the earlier (20 July 1939), Heinkel He 176. The way was paved for the next stage of the project, which now received priority status from the RLM. The Messerschmitt Me 163, a considerably refined design along the same basic lines, flew the following year.
Lippisch's designs had attracted the attention of the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM - Reich Aviation Ministry) who believed that tailless aircraft were the best basis for a rocket-powered fighter. On January 2, 1939, Lippisch and his team were transferred to the Messerschmitt company to begin work on such an aircraft, under what was known as Project X.
The DFS-194 was modified to accept a Walter R I-203 rocket engine and by October, the aircraft was undergoing engine tests at Peenemünde. These were followed by glide tests in early 1940 leading to the first powered flight in August. The flight went well, the DFS 194 reaching 550 km/h (340 mph), bettering the speed of the earlier (20 July 1939), Heinkel He 176. The way was paved for the next stage of the project, which now received priority status from the RLM. The Messerschmitt Me 163, a considerably refined design along the same basic lines, flew the following year.